An executable (.exe) file is a file or program that is executable by Microsoft Windows operating systems. However, people often face different issues with executable files like,
- Maximum GPU or CPU usage without executing the .exe file.
- A cleaning utility marks a particular executable file as harmful.
Such issues lead people to think – Whether a particular executable file is harmful to the system or not? That’s what we are going to cover here today. So, if you also want to know how to check whether an executable file is safe or not, then you’ve arrived at the right place.
Why is it Necessary to Check the Authenticity of an Executable File?
Cyber thieves often use executable files to inject malware into the system. Because sometimes, cyber thieves deliberately give their processes the same name for injecting trojan or malware into a system. The infected executable files often use extensive system resources without activating them and if that’s your case, then removing those files should be your priority.
However, executable files are not always infected. So, it’s best to check the authenticity of any executable file that looks suspicious to you.
Steps for how to Verify / Authenticate:
There are various ways to check the authenticity of an executable file. Some people use a third-party application. However, if some file is from Microsoft, then that file should have Microsoft’s digital signatures. So, we’ll check for Microsoft’s digital signatures.
Note: Here, we have picked the ‘SearchApp.exe’ file as a sample. But, you can pick any executable file and apply the same procedure there as well
Method 1: Checking Authenticity via Properties of the File
Microsoft has included its digital signature in the catalog of almost every executable file. So, the procedure for checking the digital signatures through the properties is pretty straightforward.
- First, you’ll open the ‘This PC’ window.
- Then, you’ll type the following address in the address bar of This PC’s opened window and hit the ‘Enter’ key:
C:\Windows\SystemApps\Microsoft.Windows.Search_cw5n1h2txyewy
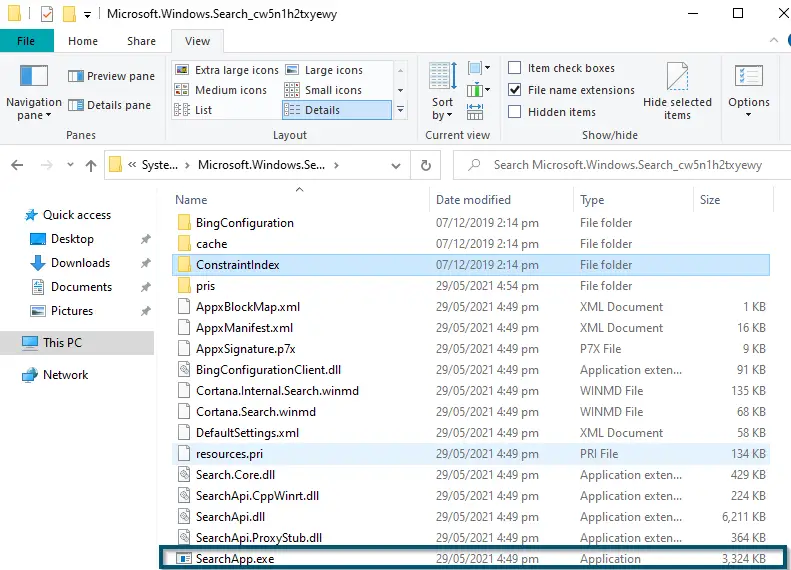
- A new window will open and now you’ll locate the ‘SearchApp.exe’ file.
Locating the ‘SearchApp.exe’ file
Note: If you’re using an older version of Windows-10 (older than 19H1 update), then look for ‘SearchUI’ instead of ‘SearchApp’
- Now, you’ll select the ‘SearchApp.exe’ file and press the ‘Alt + Enter’ keys to enter its ‘Properties’ window.
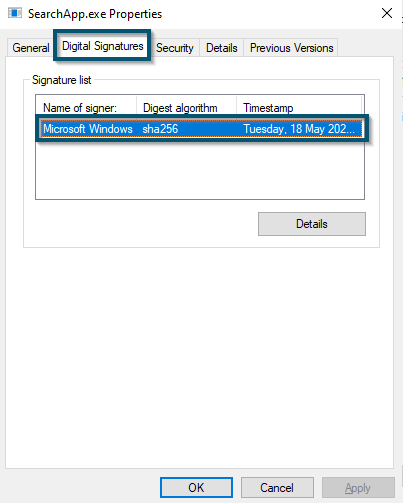
- Then, you’ll move to the ‘Digital Signatures’ tab and here you’ll find Microsoft’s ownership.
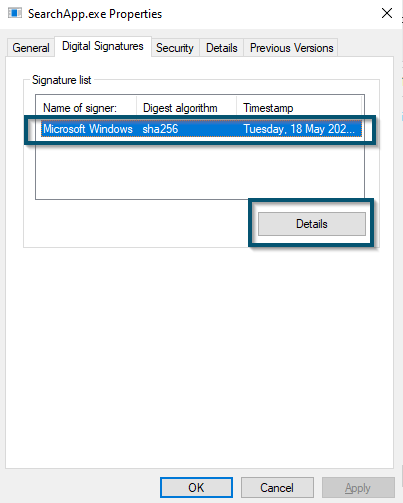
Moving to the ‘Digital Signature’ tab and finding Microsoft’s ownership - To get more information, you’ll select the signature and click on the ‘Details’ button.
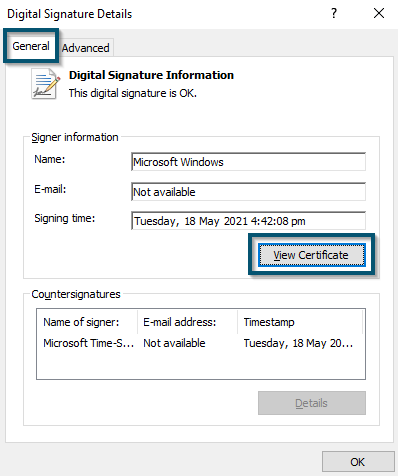
Clicking on the ‘Details’ button in the ‘Digital Signature’ Tab - A new window will open and now you’ll click on the ‘View Certificate’ button in the ‘General’ tab.
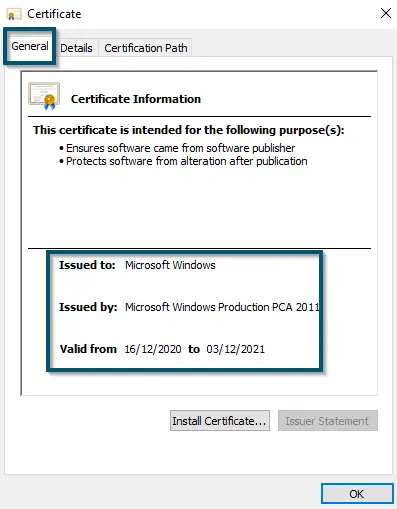
Clicking on the ‘View Certificate’ button inside the ‘General’ tab - This will open another new window and here, you’ll find Microsoft’s certification information regarding this executable file.
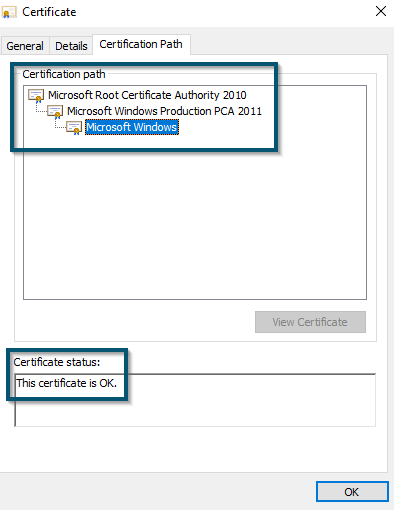
Finding Microsoft’s certificate information - You can also hover over to the ‘Certification Path’ tab and view the ‘Certificate status:’ section for verifying the certificate of this executable file.
Viewing ‘Certificate Path’ and ‘Certificate Status’
Method 2: Checking via CMD or PowerShell
If you can’t find the ‘Digital Signatures’ Tab in ‘Properties’ of Executable File
For some executable files, Microsoft doesn’t provide the digital signature information inside their catalog. So, if you’re in one such situation, then follow the steps below.
- First, you’ll follow the ‘first two steps of Method # 1’ for reaching the folder of the executable file (under-discussed).
- Now, you’ll open any browser and copy-paste the following link:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/sigcheck
- Then, you’ll press the ‘Enter’ key to open the required webpage.
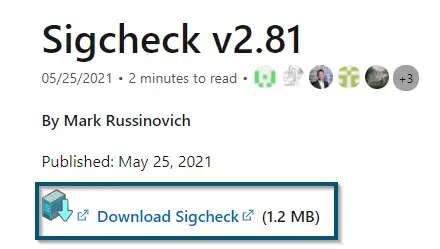
- From the new webpage, you’ll download the ‘Sigcheck’ application by clicking on the ‘Download Sigcheck’ option.
Downloading ‘Sigcheck’ - Once the download is complete, then you’ll extract the downloaded file.
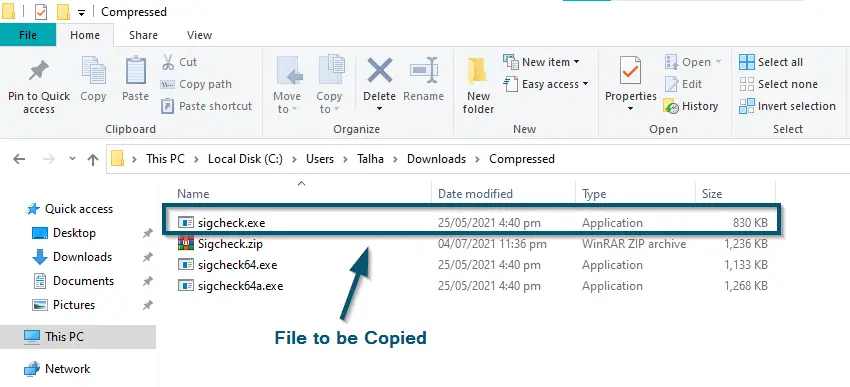
- After the extraction, you’ll select the file named ‘sigcheck’ and copy it.
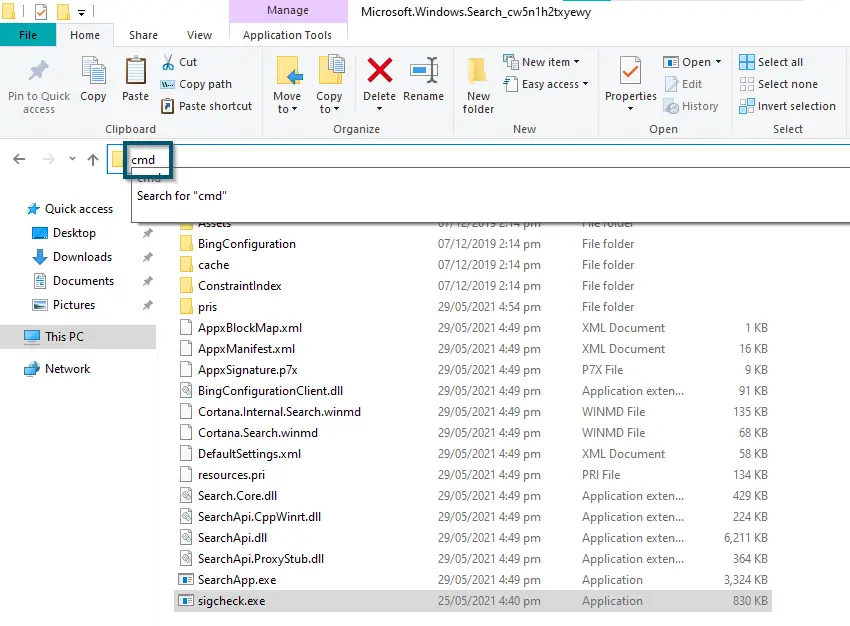
Selecting the ‘sigcheck’ file for copying - Now, you’ll paste the file inside the ‘SearchApp.exe’ folder and type ‘cmd’ in the address bar of that folder.
Typing ‘cmd’ in the address bar of the ‘SearchApp.exe’ folder - In the CMD window, you’ll type the following command and press the ‘Enter’ key to execute that command:
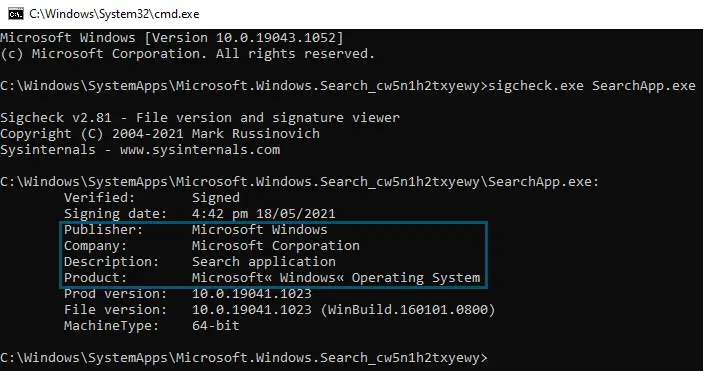
sigcheck.exe SearchApp.exe
- A new window will appear and here you’ll find the Digital Signature information of the executable file (under-discussed).
Verifying digital signatures via CMD
Method 3: Checking via Task Manager
Use Only if you don’t know the Path of the Executable File
If you don’t know the path of the running executable file, then you can check the path via Task Manager. So, try the following steps.
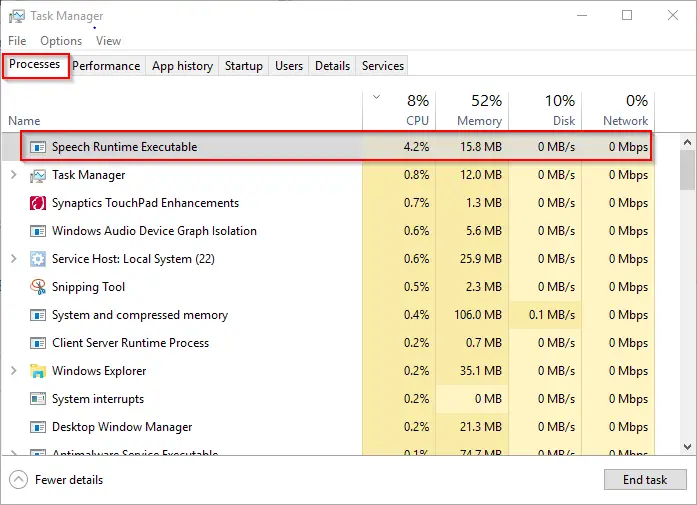
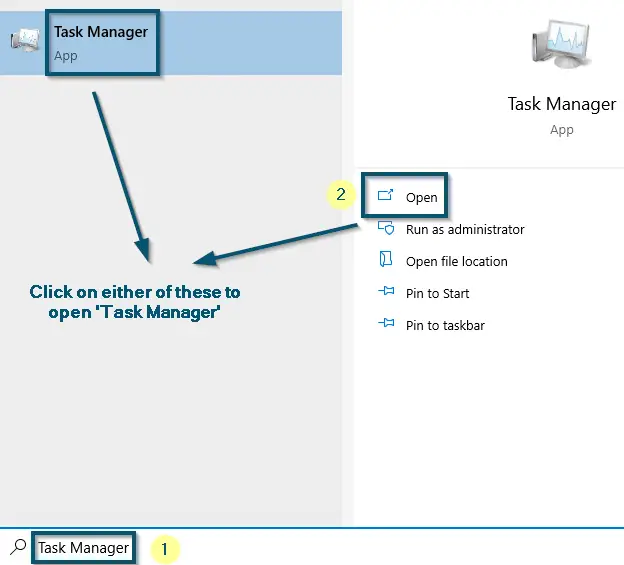
- First, you’ll open the ‘Task Manager’ by pressing the ‘Ctrl + Alt + Delete’ keys or searching in the Start Menu.
Locating ‘Speech Runtime Executable’ - Now, you’ll go to the ‘Processes’ tab and locate the required executable file.
Note: Here, we have randomly picked ‘Speech Runtime Executable.’ But you should go with the required one
- Then, you’ll right-click on it and choose the ‘Properties’ option.
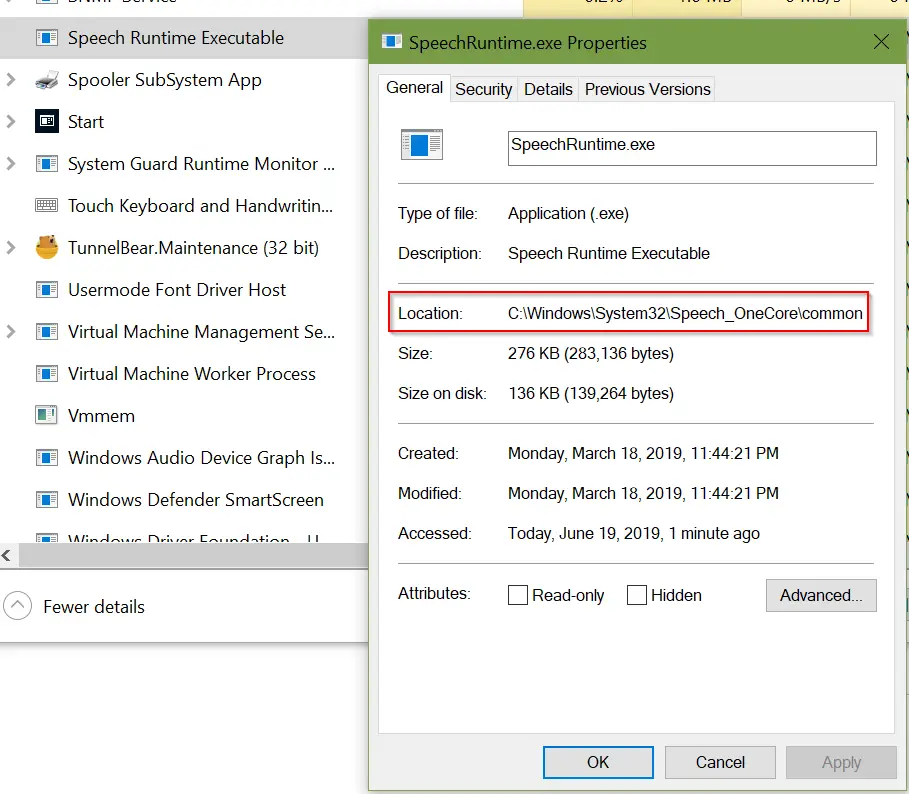
- In the ‘General’ tab, you can see the path in front of the entry named ‘Location.’
Checking path via ‘Task Manager’ - Now, you’ll ‘follow Method # 1 or 2’ for completing the rest of the procedure of how to tell if a program is a virus or not.
Method 4: Scanning using Antivirus
Sometimes, companies don’t provide the digital signature information of a file. If you are unable to verify using a digital signature, you can scan the file using an antivirus. For scanning an executable file, you can use any antivirus application. But here, we will use ‘Microsoft Windows Defender’ for checking any executable file for viruses.
Note: We will perform this operation for the ‘AdobeARM.exe’ file. But you can do the same for any executable file
- Open the ‘Task Manager’ on your system.
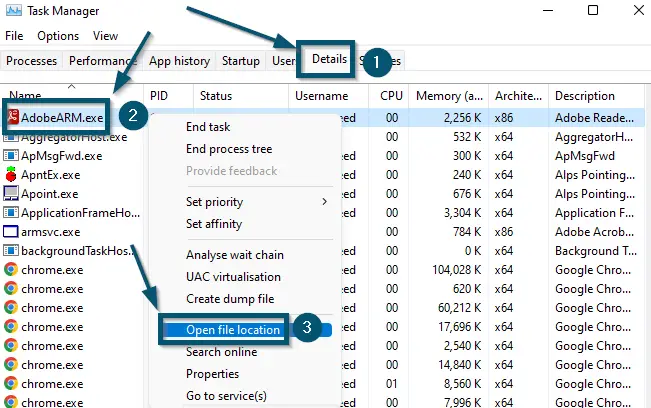
Opening the ‘Task Manager’ from the ‘Start menu’ - Then, switch to the ‘Details’ tab.
- Scroll down to find the process or file that you are investigating.
- Then, select and right-click on the ‘Open file location’ option. Doing this will take you to the root folder of the file.
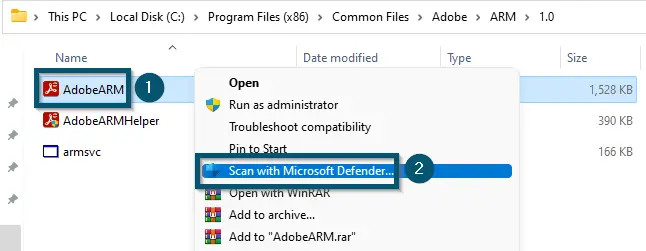
Switching to the ‘Details’ tab, right-clicking on the ‘AdobeARM.exe’ process and choosing the ‘Open file location’ option - Now, right-click on the ‘AdobeARM’ file and choose the ‘Scan with Microsoft Defender…’ option.
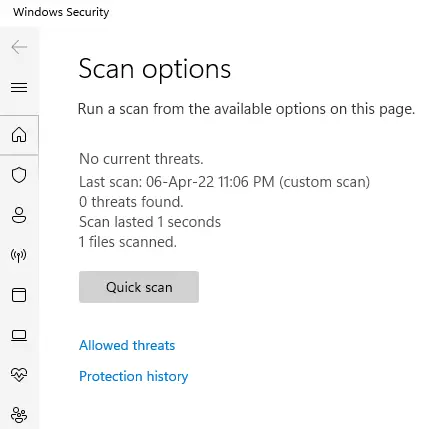
Right-Clicking on the ‘AdobeARM’ (executable) file and choosing the ‘Scan with Microsoft Defender…’ option - Windows Security (Defender) will scan this executable file and show the results within a few seconds.
Results of the Scanning of Windows Security (Defender) for the ‘AdobeARM’ (Executable) File
Conclusion
If you’ve followed all the methods and your signature information is similar to the provided information, then your executable file is safe.
However, your executable file will be dangerous for the system in the following scenarios:
- If you find a suspicious directory in the ‘General’ tab of the executable file’s properties.
OR
- If you find any other ownership in the ‘Details’ tab of the executable file’s properties.
OR
- If the file is using too many GPU and CPU resources. Because often .exe files containing malware are using most of the system’s resources without opening it.
But if you want to know how to check if a file is safe before downloading or how to check if a file has a virus before downloading, then a top browser like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, or Safari can automatically tell that a particular file is safe to download or not.